Services
Hysteroscopy surgeries
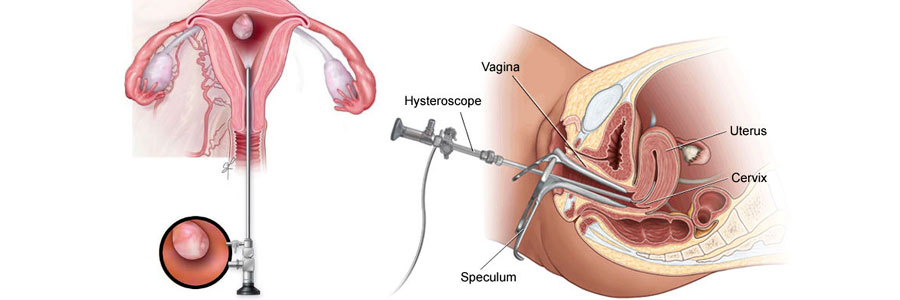
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the uterus. During a hysteroscopy, a thin, lighted telescope-like instrument called a hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. This allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the uterus and perform procedures without making any incisions.
Here's an overview of hysteroscopy surgeries and consultations:
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy: This procedure is primarily used to diagnose the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding, recurrent miscarriages, or infertility. The hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus, and the doctor examines the uterine cavity for abnormalities such as polyps, fibroids, adhesions (scar tissue), or structural abnormalities.
- Operative Hysteroscopy: In this type of hysteroscopy, surgical instruments are passed through the hysteroscope to perform various procedures to treat the identified abnormalities. Some common operative hysteroscopy procedures include:
- Polypectomy: Removal of uterine polyps, which are overgrowths of tissue in the uterine lining.
- Myomectomy: Removal of uterine fibroids (non-cancerous growths) that are inside the uterine cavity.
- Endometrial Ablation: Destruction or removal of the uterine lining, typically used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Septum Resection: Correction of a uterine septum, a condition where there is a band of tissue dividing the uterine cavity.
- Adhesiolysis: Removal of intrauterine adhesions (scar tissue) that may be causing infertility or menstrual irregularities.
- Consultation Process:
- Patient History: The consultation begins with a thorough review of the patient's medical history, including symptoms, previous surgeries, and any relevant medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: A pelvic examination may be performed to assess the size and position of the uterus and to check for any abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the patient's symptoms, diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, hysterosalpingography (HSG), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to further evaluate the uterus and surrounding structures.
- Discussion of Options: Once a diagnosis is made, the doctor will discuss treatment options with the patient, including the possibility of hysteroscopy surgery if indicated.
- Preparation for Surgery: If surgery is recommended, the patient will be given instructions on how to prepare for the procedure, which may include fasting before surgery and stopping certain medications.
- Follow-up: After the surgery, the patient will have follow-up appointments with their doctor to monitor recovery and ensure that the treatment was successful.
