Services
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome)
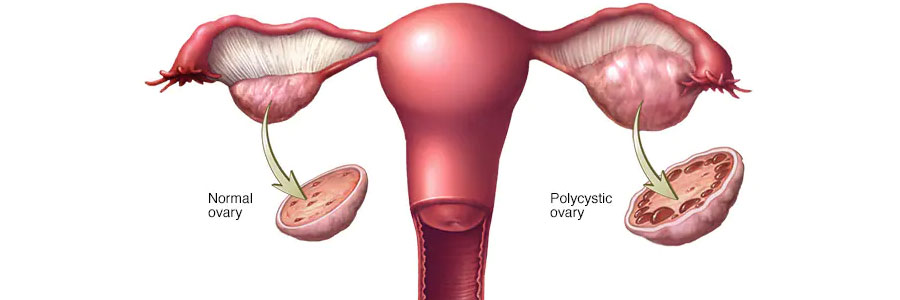
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting people with ovaries, typically during their reproductive years. PCOS is characterized by a combination of symptoms related to hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
Here's an overview of PCOS:
Symptoms:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with PCOS may experience irregular periods, which can range from infrequent or prolonged menstrual cycles to complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Ovulatory dysfunction: PCOS can disrupt ovulation, leading to difficulty conceiving (infertility) or reduced fertility.
- Hyperandrogenism: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) can cause symptoms such as hirsutism (excess hair growth on the face, chest, or back), acne, and male-pattern baldness (androgenic alopecia).
- Polycystic ovaries: Multiple small cysts (follicles) may develop on the ovaries, detected through imaging studies such as ultrasound.
- Other symptoms: Additional symptoms may include weight gain or difficulty losing weight, insulin resistance, metabolic abnormalities (such as high blood sugar or cholesterol levels), skin changes (acanthosis nigricans), and mood disturbances.
Causes:
- The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood but likely involves a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
- Insulin resistance: Many individuals with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated insulin levels and increased androgen production by the ovaries.
- Hormonal imbalances: PCOS is characterized by disturbances in the production and regulation of hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and androgens, which can affect ovarian function and menstrual cycles.
Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of PCOS is typically based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
- Diagnostic criteria may include the presence of irregular menstrual cycles, signs of hyperandrogenism (such as hirsutism or acne), and ultrasound findings of polycystic ovaries.
- Other conditions that mimic PCOS, such as thyroid disorders or adrenal gland disorders, should be ruled out through appropriate testing.
