Services
Laparoscopy Surgeries
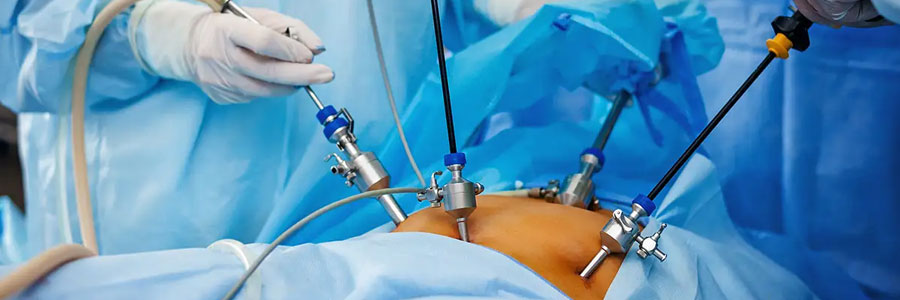
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique used to diagnose and treat a variety of abdominal and pelvic conditions. It involves making small incisions through which a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted, allowing the surgeon to visualize and operate inside the abdomen or pelvis.
Here's an overview of laparoscopy surgeries and the consultation process:
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is used to investigate the cause of abdominal or pelvic symptoms such as pain, infertility, or abnormal bleeding.
- During the procedure, the laparoscope is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen, providing a clear view of the pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding structures.
- The surgeon examines the organs for abnormalities such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, fibroids, adhesions, or structural abnormalities.
- Operative Laparoscopy: Operative laparoscopy involves performing surgical procedures using specialized instruments inserted through small incisions. Common operative laparoscopic procedures include:
- Ovarian Cystectomy: Removal of ovarian cysts.
- Salpingectomy or Salpingo-oophorectomy: Removal of fallopian tubes or ovaries.
- Myomectomy: Removal of uterine fibroids.
- Treatment of Endometriosis: Excision or ablation of endometrial implants.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus.
- Tubal Ligation: Surgical sterilization by blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes.
- Consultation Process:
- Medical History: The consultation begins with a detailed review of the patient's medical history, including symptoms, previous surgeries, and any relevant medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: A pelvic examination may be performed to assess the size and position of the uterus and ovaries and to check for any abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the patient's symptoms, diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or blood tests may be recommended to further evaluate the pelvic organs.
- Discussion of Options: Once a diagnosis is made, the doctor will discuss treatment options with the patient, including the possibility of laparoscopic surgery if indicated.
- Preparation for Surgery: If surgery is recommended, the patient will be given instructions on how to prepare for the procedure, which may include fasting before surgery and stopping certain medications.
- Follow-up: After the surgery, the patient will have follow-up appointments with their doctor to monitor recovery and ensure that the treatment was successful.
